43 stratified squamous epithelium labeled diagram
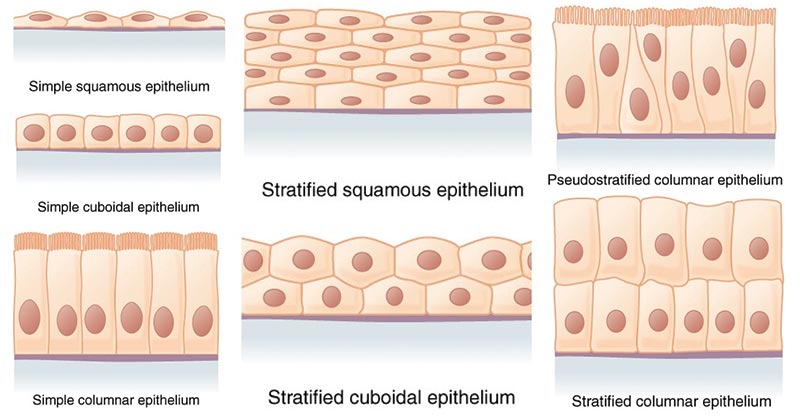
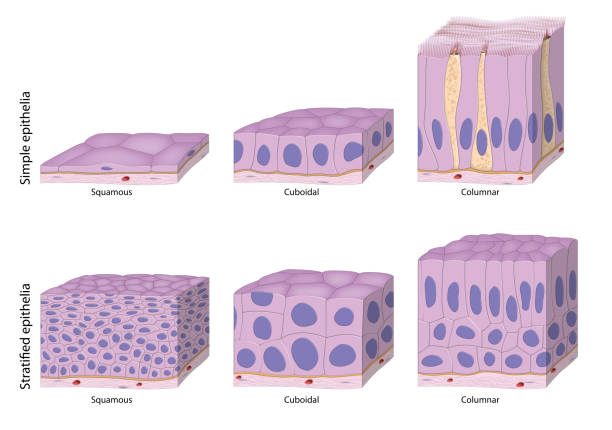
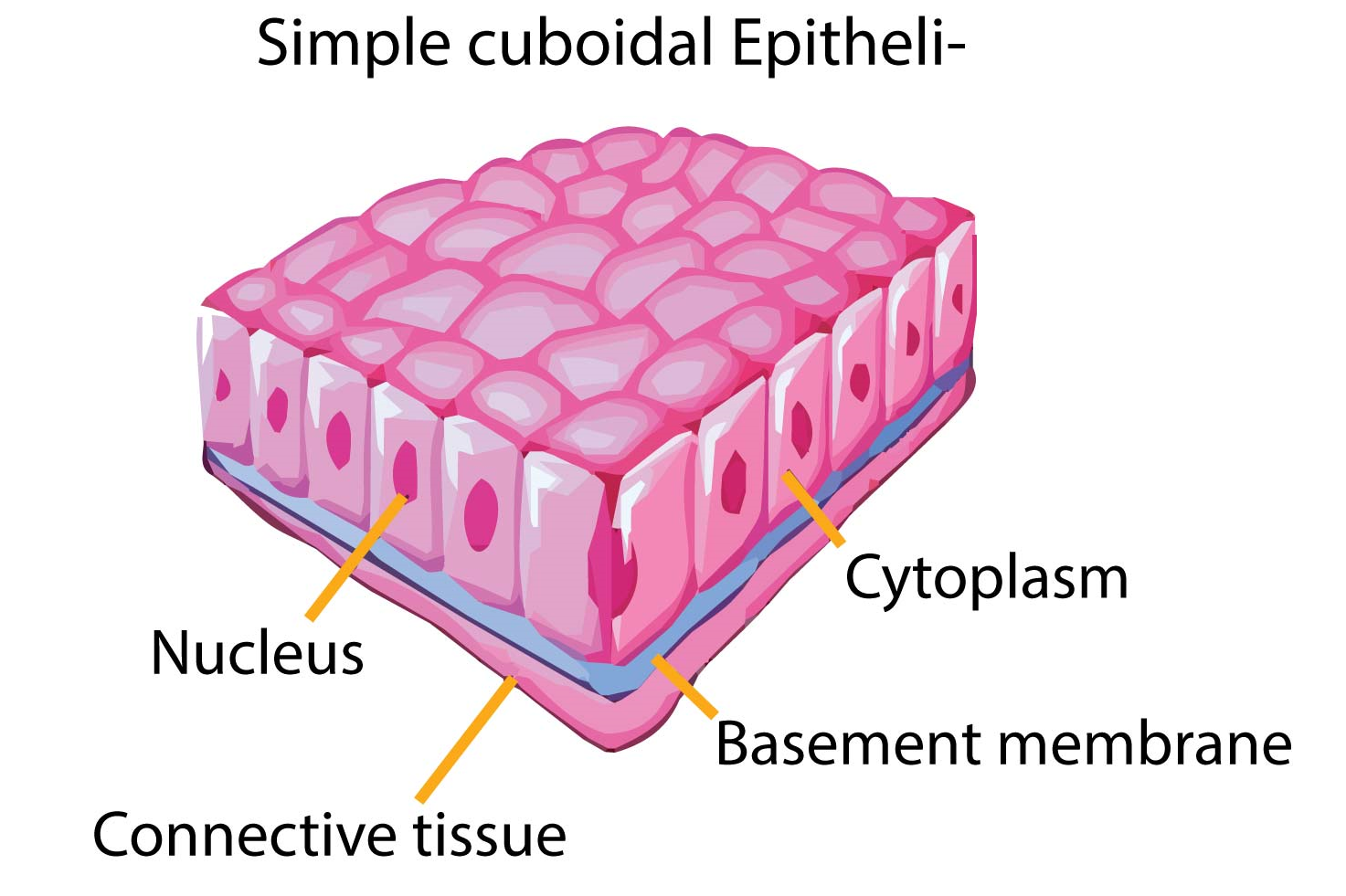
Stratified cuboidal Stratified squamous Transitional Epithelium with single layer of cube-shaped cells. Epithelium with multiple layers of tall, thin cells. Epithelium with layers of cells that appear cubelike when an organ is relaxed and flattened when the organ is distended by fluid. Epithelium with single layer of flat, often hexagonal cells. The stratified squamous epithelium is the tissues which are formed by multiple layers of cells on resting basement membrane with superficial layer contain squamous cells. Underlying cell layers can compose of cuboidal or columnar cells.
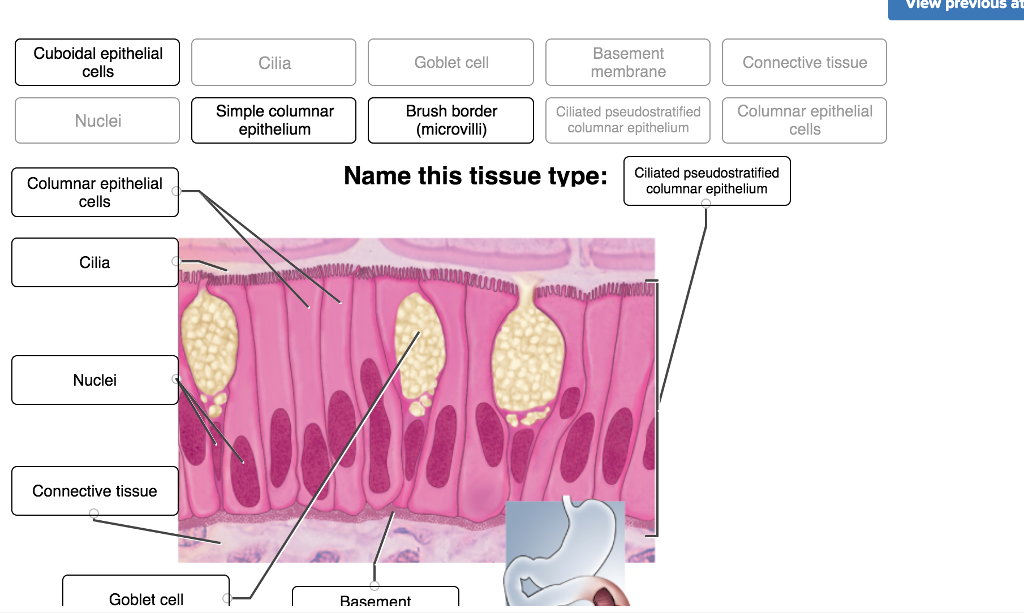
A. Simple columnar epithelium. Slide 29 (small intestine) View Virtual Slide Slide 176 40x (colon, H&E) View Virtual Slide Remember that epithelia line or cover surfaces. In slide 29 and slide 176, this type of epithelium lines the luminal (mucosal) surface of the small and large intestines, respectively. Refer to the diagram at the end of this chapter for the tissue orientation and consult ...
Stratified squamous epithelium labeled diagram
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Function. The function of stratified squamous epithelium is to protect the tissues and organs they cover as they are continually exposed to stress and friction. The ability of the stratified squamous epithelium to regenerate quickly helps it to best serve this function. Slide diagram of the tongue showing the ... This video describes how to draw stratified squamous non keratinized epithelium histology diagram. The epithelial lining at the entrance (vestibule) to the nasal cavity exhibits a gradual change from keratinized stratified squamous epithelium of the skin in the nasal vestibule (shown in slide 124F) View Image, to the pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium that is characteristic of the nasal mucosa posterior to the vestibule (shown in ...
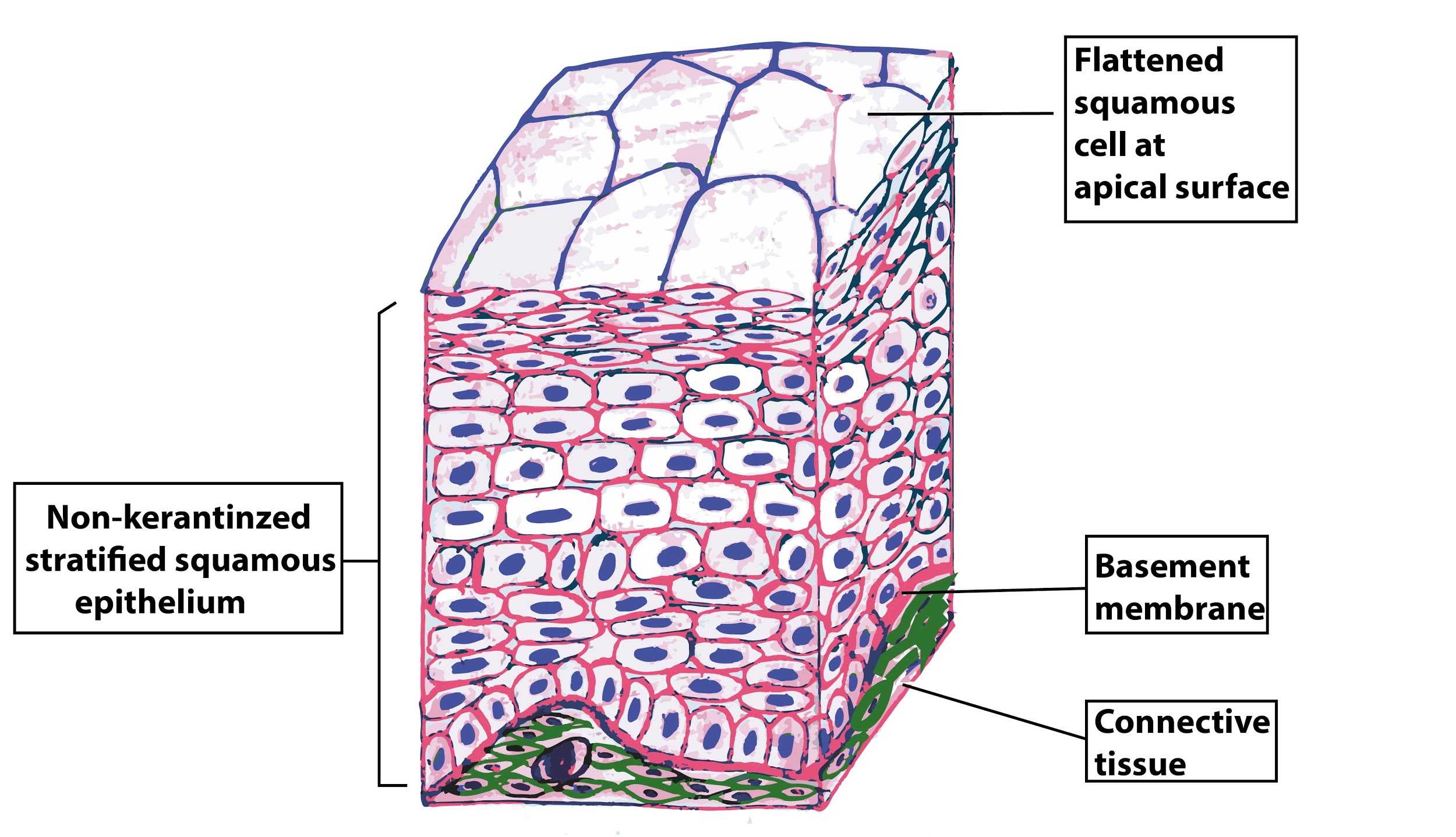
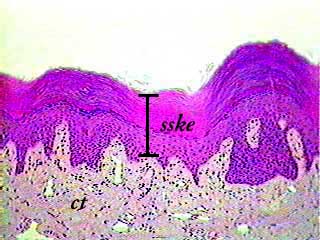
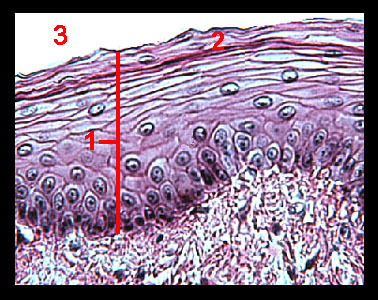
Stratified squamous epithelium labeled diagram. A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane.Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural integrity. Although this epithelium is referred to as squamous, many cells within the layers may not be flattened; this is due to the convention of ... Apr 28, 2017 · A stratified squamous epithelium is a tissue formed from multiple layers of cells resting on a basement membrane, with the superficial layer(s) consisting of squamous cells. Underlying cell layers can be made of cuboidal or columnar cells as well. Diagram of a nonkeratinizing stratified squamous epithelium A stratified squamous epithelium consists of more than one (typically many) layers, or strata, of epithelial cells (see figure). The basal layer of epithelial cells are small and cuboidal-to-columnar; the cells gradually become larger and more squamous as the cells migrate from the ... Start studying ANATOMY TISSUES LABELING. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
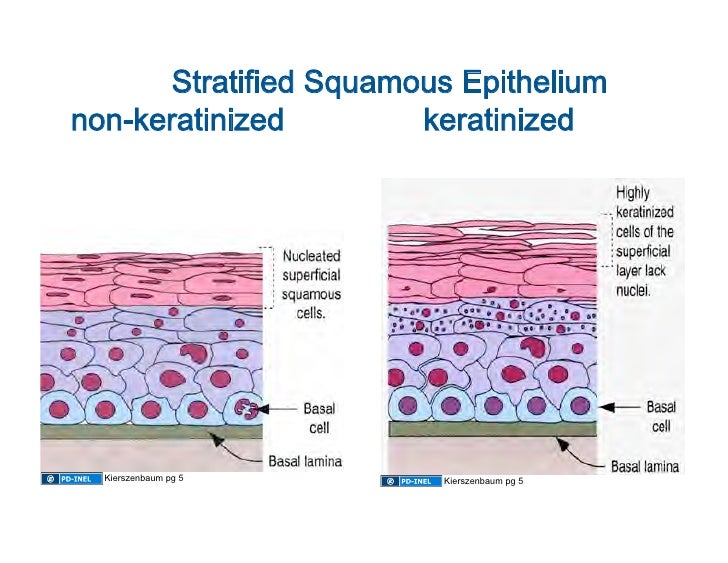
Sep 28, 2020 · Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium is a type of stratified squamous epithelium in which the cells have a tough layer of keratin in the apical segment of cells and several layers deep to it. Keratin is a tough, fibrous intracellular protein that helps protect skin and underlying tissues from heat, microbes, and chemicals. Squamous- thin and flat cells. Cuboidal- short cylindrical cells, which appear hexagonal in cross-section. Columnar- long or column-like cylindrical cells, which have nucleus present at the base. On the basis of the number of layers present, epithelial tissue is divided into the simple epithelium and stratified or compound epithelium Non-Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium B Mb. Identify the structure indicated. Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium Basement membrane. Identify the tissue type and a location where it is found. Non-Keratinized Stratified Squamous •Esophagus • MouthEpithelium• Vagina. Stratified squamous epithelium (keratinized) lining in the mucosa or papillae of rumen slide. Stratum corneum cell layers (variable thickness) and others; I hope the rumen slide labeled diagram might help you find out the structures mentioned above easily. Rumen histology slide identification points
Apr 20, 2019 · Squamous. stratified squamous diagram photo of endothelial cells. Squamous means scale-like. simple squamous. Bodytomy provides a labeled diagram to help you understand the structure and Simple Columnar Epithelium: Labeled Diagram and Function. Epithelium is a tissue that lines the internal surface of the body, as well as the internal organs. Simple epithelium is one of the types of epithelium that is. Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium 40X (Palmar skin) Although stratified squamous keratinized epithelium covers the entire surface of the body, most of it also includes hair, which makes the basic tissue structure harder to see. If we just want to look at stratified squamous keratinized epithelium, we look at skin from one of the few ... Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium (400X), surface This image shows only the outermost layers of the stratified squamous epithelium. The cells in this tissue are not all squamous (flat). It is named for the shape of the cells on the surface of the tissue. The arrow indicates one of these squamous cells. These labelled diagrams should closely follow the current Science courses in histology, anatomy and embryology and complement the virtual microscopy ... (keratinised stratified squamous epithelium) ORIGIN: ectoderm lamina propria SKIN Covers the external surface.
The corneal epithelium is composed fairly uniformly of 5-7 layers of cells [Fig. 3]. It is about 50 μ in thickness. The epithelium is uniform to provide a smooth regular surface and is made up of nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium. The epithelium is derived from surface ectoderm between 5 and 6 weeks of gestation.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium (Diagram) Simple Cuboidal Epithelium (Diagram) Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium (Diagram) ... Cranial Nerves-Anatomy 12 Terms. kajcolarusso TEACHER. Peripheral Nerves 18 Terms. kajcolarusso TEACHER. THIS SET IS OFTEN IN FOLDERS WITH... Epithelial Basics 10 Terms.
Dec 25, 2020 · 13 Best Stratified Squamous Epithelium Images Stratified. The Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium Of The Tongue. Epithelium Stock Pictures Royalty Free Photos Images Getty Images. Examining Epithelial Tissue Under The Microscope Human Anatomy.
FIGURE 1-1 (a) Simple squamous epithelium lines the lumina of vessels, where it permits diffusion.(b) A photomicrograph of this tissue and (c) a labeled diagram.Simple squamous epithelia that line the lumina of vessels are referred to as endothelia, and that which cover visceral organs are referred to as mesothelia.
Epithelium is a tissue that lines the internal surface of the body, as well as the internal organs. Simple epithelium is one of the types of epithelium that is divided into simple columnar epithelium, simple squamous epithelium, and simple cuboidal epithelium. Bodytomy provides a labeled diagram to help you understand the structure and function of simple columnar epithelium.
A stratified squamous epithelium is a stratified epithelium with squamous (flattened and scale-like) epithelial cells in the top layer. Cuboidal or columnar cells may be seen in the deeper layers. Some stratified squamous epithelia are extensively keratinized, whereas others are keratinized either minimally or not at all.
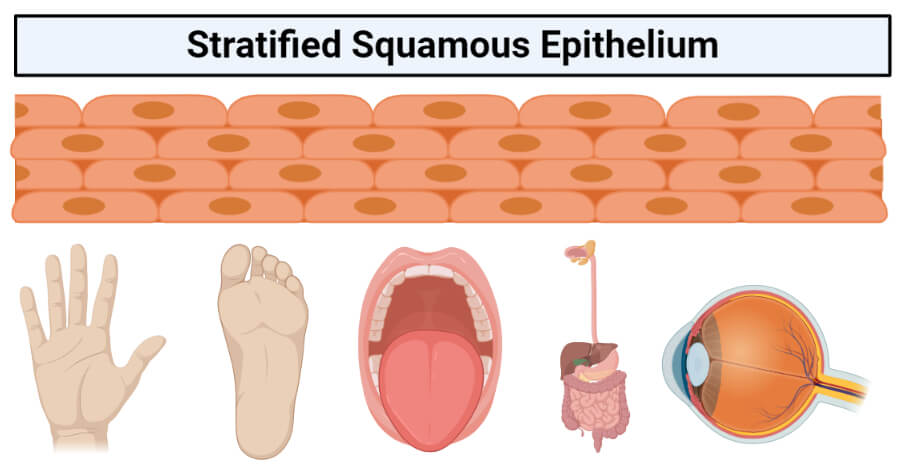
Aug 23, 2021 · The stratified squamous epithelium lines the surface of the tongue, the hard upper palate of the mouth, the oesophagus, and the anus in the digestive system. It can also be found in female reproductive organs such as the vagina, cervix, and labia majora. Stratified epithelium also lines the upper respiratory system, which may come into touch ...
The simple squamous epithelium is different from other types of epithelial tissue such as simple cuboidal, simple columnar, and stratified squamous epithelium in that it is only made of one layer ...
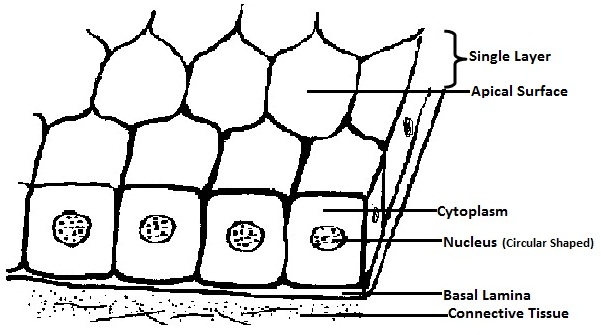
Simple Squamous Epithelium (Figure 4.3a) A simple squamous epithelium is a single layer of flat cells. When viewed from above, the closely fitting cells resemble a tiled floor. When viewed in lateral section, they resemble fried eggs seen from the side. Thin and often permeable, this type of epithelium occurs wherever small molecules pass through
Learn to draw Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium histology diagram ( For MBBS and BDS students)
For squamous stratified epithelium, there is a third sub-classificational feature: the keratinization, or lack thereof, of the apical surface domains of the cells. A typical example of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium is the epidermis. Function. The function of stratified epithelium is mainly protection. In fact, this specific role is ...
Form the Outer Covering of the skin and some internal organs. Form the Inner Lining of blood vessels, ducts and body cavities, and the interior of the respiratory, digestive, urinary and reproductive systems. Glandular epithelia. Constitute the secretory portion of glands. Simple squamous epithelium. Most delicate epithelium.
Stratified squamous epithelium is the most common type of stratified epithelium in the human body. The apical cells appear squamous, whereas the basal layer contains either columnar or cuboidal cells. The top layer may be covered with dead cells containing keratin. The skin is an example of a keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium.
The epithelial lining at the entrance (vestibule) to the nasal cavity exhibits a gradual change from keratinized stratified squamous epithelium of the skin in the nasal vestibule (shown in slide 124F) View Image, to the pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium that is characteristic of the nasal mucosa posterior to the vestibule (shown in ...
This video describes how to draw stratified squamous non keratinized epithelium histology diagram.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Function. The function of stratified squamous epithelium is to protect the tissues and organs they cover as they are continually exposed to stress and friction. The ability of the stratified squamous epithelium to regenerate quickly helps it to best serve this function. Slide diagram of the tongue showing the ...





:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/stratified-epithelium/kxsJZMc6RS4j61ethfEOw_A4WBRjTb2LJJRtmn2wVxCw_stratified_squamous_epithelia02.png)


















Comments
Post a Comment